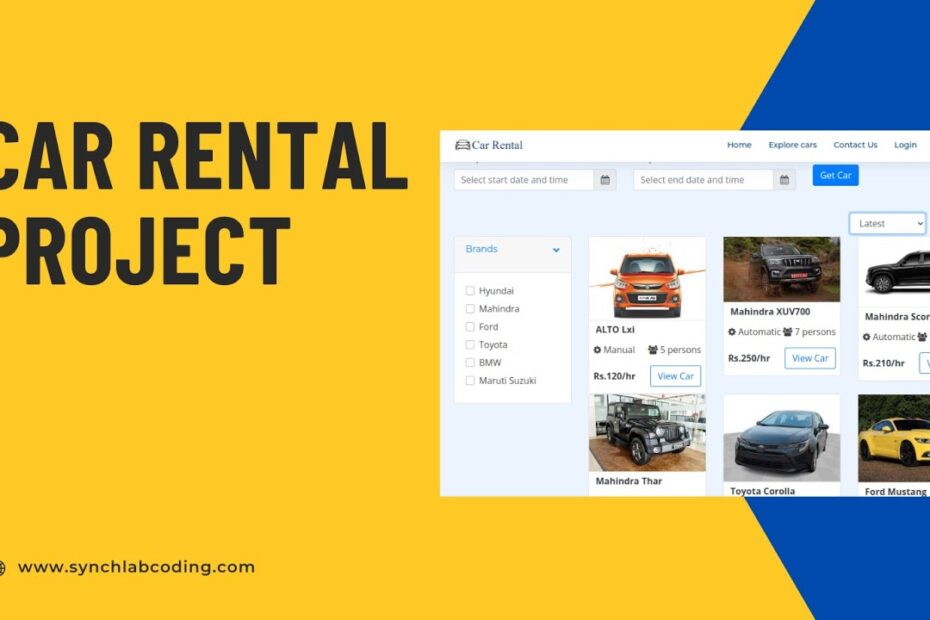
What is a Vehicle Rental Management System Using PHP and MySQL?
A Vehicle Rental Management System using PHP and MySQL is basically the tech-savvy sidekick for car rental businesses, turning what could be a chaotic parade of keys and contracts into a smoothly oiled machine—pun absolutely intended. Picture this: PHP handles the behind-the-scenes magic, like processing user requests and whipping up dynamic web pages, while MySQL keeps all the data organized in a database that’s as reliable as a trusty old sedan. It’s not just about renting out wheels; it’s about streamlining everything from customer bookings to inventory checks, all with a dash of code that makes you wonder why we ever relied on spreadsheets and sticky notes.
This system shines by tackling everyday rental headaches with features that are both practical and oddly entertaining, like preventing double-bookings that could lead to awkward “oops, that car’s already gone” moments. For instance, here’s a quick rundown of its core components:
- Handling user registrations and vehicle searches to make finding the perfect ride as easy as scrolling through your phone.
- Managing rental agreements and payments, ensuring secure data storage with MySQL’s robust querying.
All in all, it’s the digital equivalent of a rental agent who’s always on time and never forgets a detail.
How to Build a Vehicle Rental Management System with PHP and MySQL
Diving into building a vehicle rental management system with PHP and MySQL is like trying to rent out a sports car to a grandma—exciting but full of unexpected twists, like debugging code at 2 a.m. because your script decided to “rent” a vehicle to a fictional character from a sci-fi novel. Start by setting up your MySQL database to track essentials like vehicle details, customer info, and rental history; think of it as organizing a chaotic garage so you don’t accidentally hand over the keys to a rusty bicycle when someone asks for a luxury SUV. With PHP, you’ll handle the backend magic, creating forms for booking and returning vehicles, while throwing in some validation checks to ensure no one tries to rent a car for a million years or forgets to return it altogether—because let’s face it, who needs a system that lets users vanish with your fleet?
Now, to keep things rolling without any comedic crashes, here’s a quick rundown of key steps in an unordered list that’ll make your project hum like a well-tuned engine:
- Set up your MySQL tables for vehicles, customers, and rentals, ensuring you include fields like vehicle ID, availability status, and rental dates to avoid double-booking debacles.
- Use PHP to connect to the database with secure queries, adding features like search functions so users can filter by vehicle type or price—nothing says funny like searching for a “flying car” that doesn’t exist.
Remember, blending these tools means your system won’t just manage rentals; it’ll do it with a wink, preventing mishaps like renting out a truck to a hamster enthusiast.